Median Household Income
The wages and cash benefits that members of a household earn before paying taxes
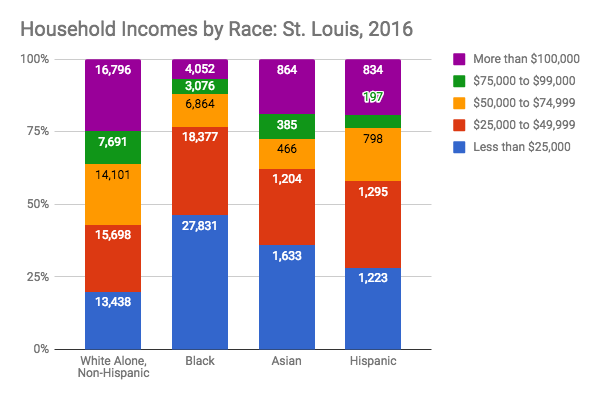
White households’ median income is nearly twice that of black households.
A score of 100 represents racial equity, meaning there are no racial disparities in outcomes. The lower the Equity Score, the greater the disparity.
For Median Household Income, a score of 100 — a score reflecting racial equity — would mean black households and white households have the same median income. It is important to note that for this indicator, equity is not our only goal; we also want to improve outcomes for all.
More Information
What does this indicator measure?
Median Household Income measures all the wages and cash benefits that members of a household earn before paying taxes. In 2016, the median household income in the City of St. Louis was $42,000.
Median household income analysis
Median household income in St. Louis City.
| All | White | Black | Disparity Ratio | Equity Score | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median household income | $42,000 | $55,000 | $28,000 | 1.964 to 1 | 42 |
Data Source: American Community Survey 1-year PUMS, 2016.
What does this analysis mean?
The median household income for white households in St. Louis is nearly twice that of black households. White households have the highest median income of $55,000. Black households have the lowest median income of $28,000, followed by Hispanic households with $34,200. If median income were equitable, black households’ median income would be $27,000 more per year.
Data Note: PUMS data may differ slightly from estimates on American FactFinder due to differences in sampling. See PUMS technical documentation for more information. Median is a statistical measure to find the midpoint of a large set of data. In this case, half of households of each race in St. Louis earn more than the median, and half earn less. Estimates for Hispanic residents are based on a small number of sample cases and should be interpreted with extreme caution. The number of sample cases is too small to report reliable estimates for additional racial groups.
Why does Median Household Income matter?
Median Household Income is an important measure of economic health that helps account for extreme changes at either end of the income spectrum, such as the increasing concentration of poverty and wealth. People with lower median household incomes compared to other households in their region have greater difficulty in finding affordable housing and affordable childcare. The Ferguson Commission report shared an estimate from the University of Missouri-St. Louis Public Policy Research Center’s Equity Assessment that “eliminating racial income gaps would boost the St. Louis economy by $14 billion.” See the next two indicators for greater insight: Adult Poverty and High-Wage Occupations.
Which Calls to Action from the Ferguson Commission report are linked with this indicator?
The Ferguson Commission’s calls to action related to income include:
Questions for further investigation
- Why is there a racial disparity in Median Household Income?
- What can St. Louis do to reduce racial disparities in Median Household Income?
- What initiatives are currently underway to reduce racial disparities in Median Household Income?